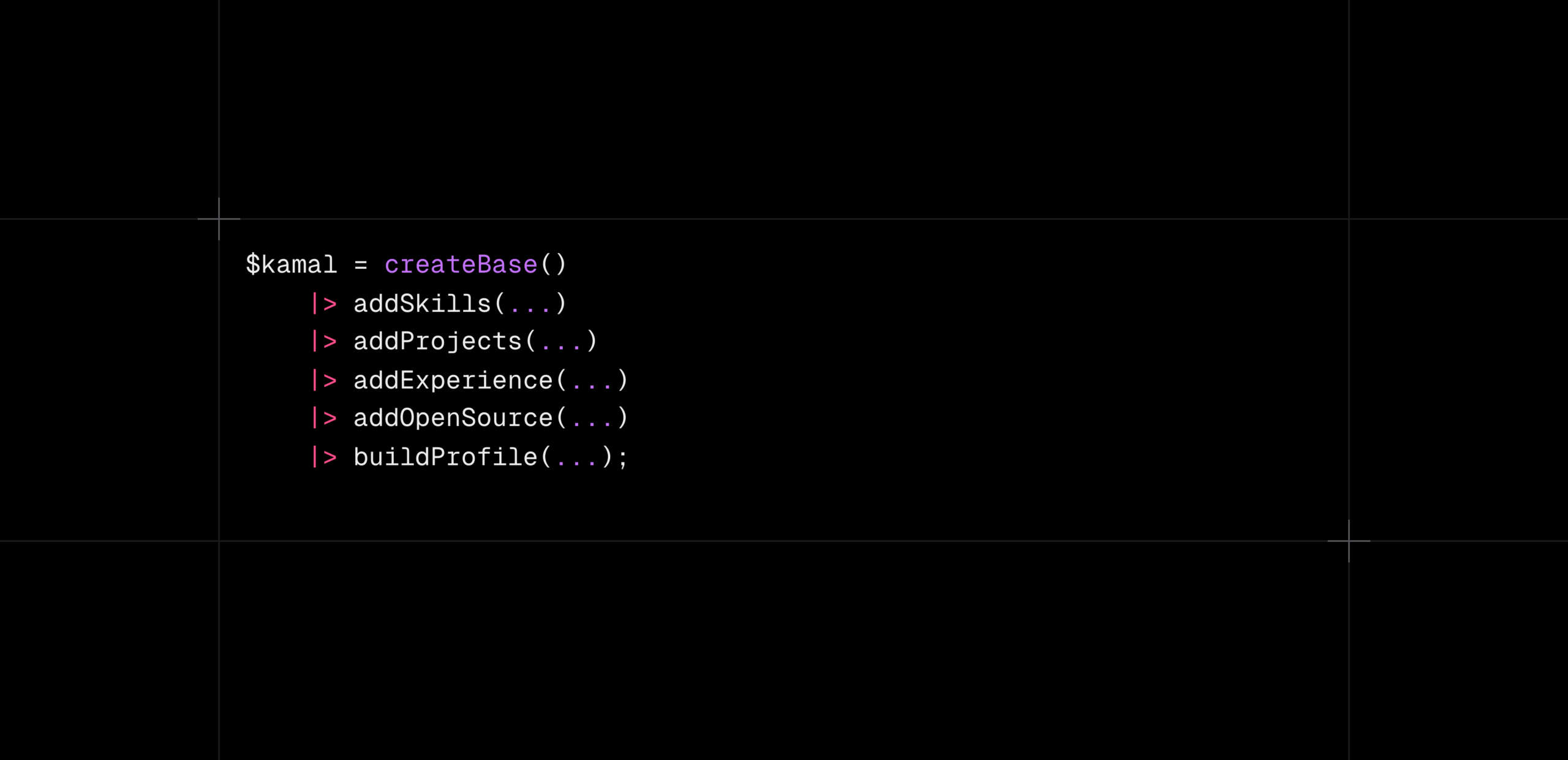
The pipe operator (|>) is a powerful addition coming in PHP 8.5 that enables clean and readable chaining of functions. Inspired by functional programming, it simplifies the process of applying multiple transformations to a value by passing the result of one expression directly into the next. This helps avoid deep nesting and makes code easier to read and maintain.
The pipe operator takes the value on the left side and passes it as the only argument to the callable on the right side. It supports:
The right-hand callable must accept exactly one parameter.
$donut = addCrumbs(
addChocolate(
addMarshmallow(
addHearts(
addSprinkles(
addIcing(
bakeDonut()
)
)
)
)
)
);
$donut = bakeDonut()
|> addIcing(...)
|> addSprinkles(...)
|> addHearts(...)
|> addMarshmallow(...)
|> addChocolate(...)
|> addCrumbs(...);
This linear flow improves readability and reflects the natural order of operations.
$output = $input
|>trim(...)
|> fn(string $s) => str_replace(' ', '-', $s)
|> fn(string $s) => str_replace(['.', '/', '…'], '', $s)
|> strtolower(...);
Each function receives the output of the previous one, eliminating the need for temporary variables.
The pipe operator brings clarity to PHP code, making it easier to work with complex transformations. It is a welcome feature for developers aiming to write more expressive and maintainable code.

I’m Kamal, a WordPress developer focused on plugins, APIs, and scalable products.
Learn More